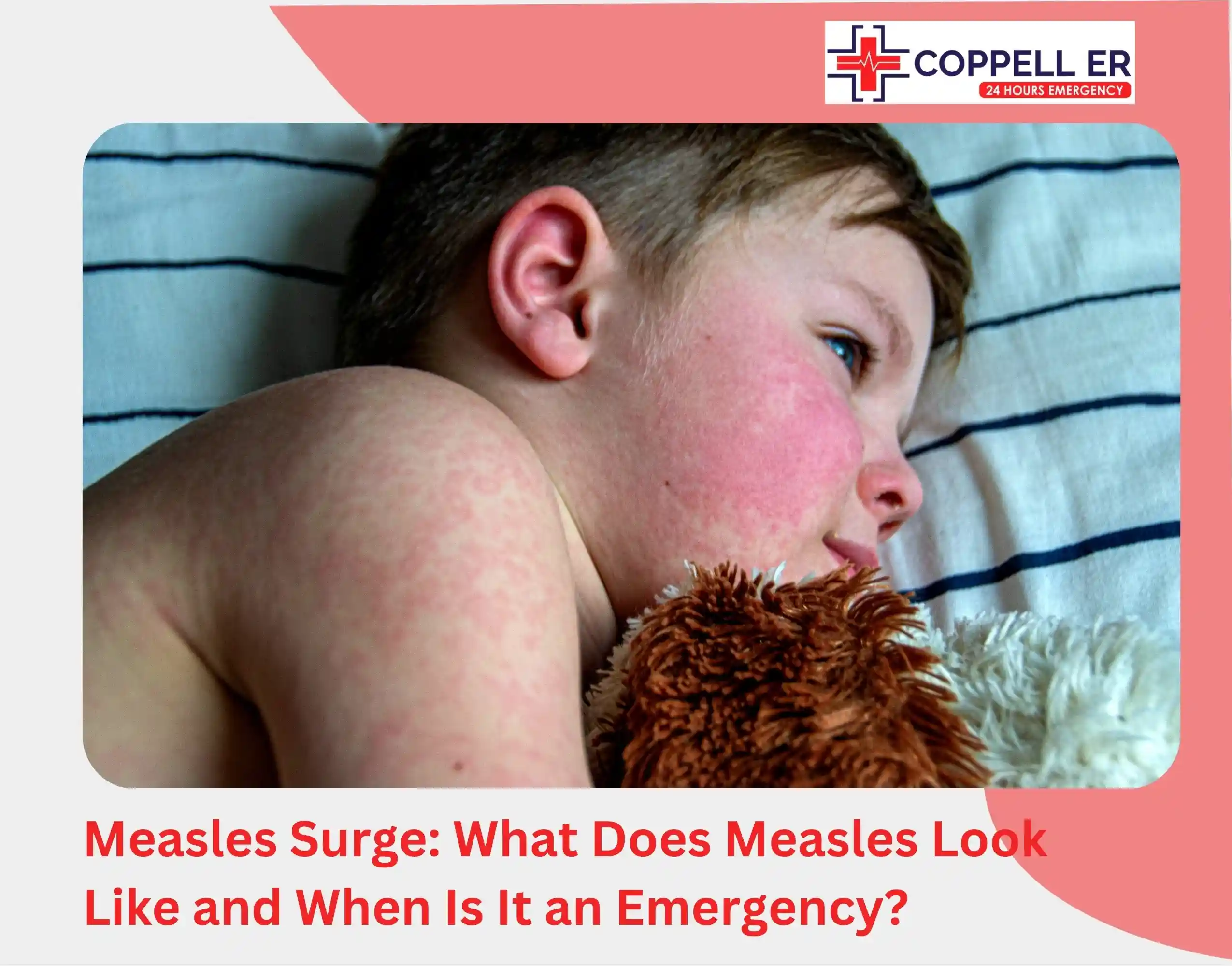
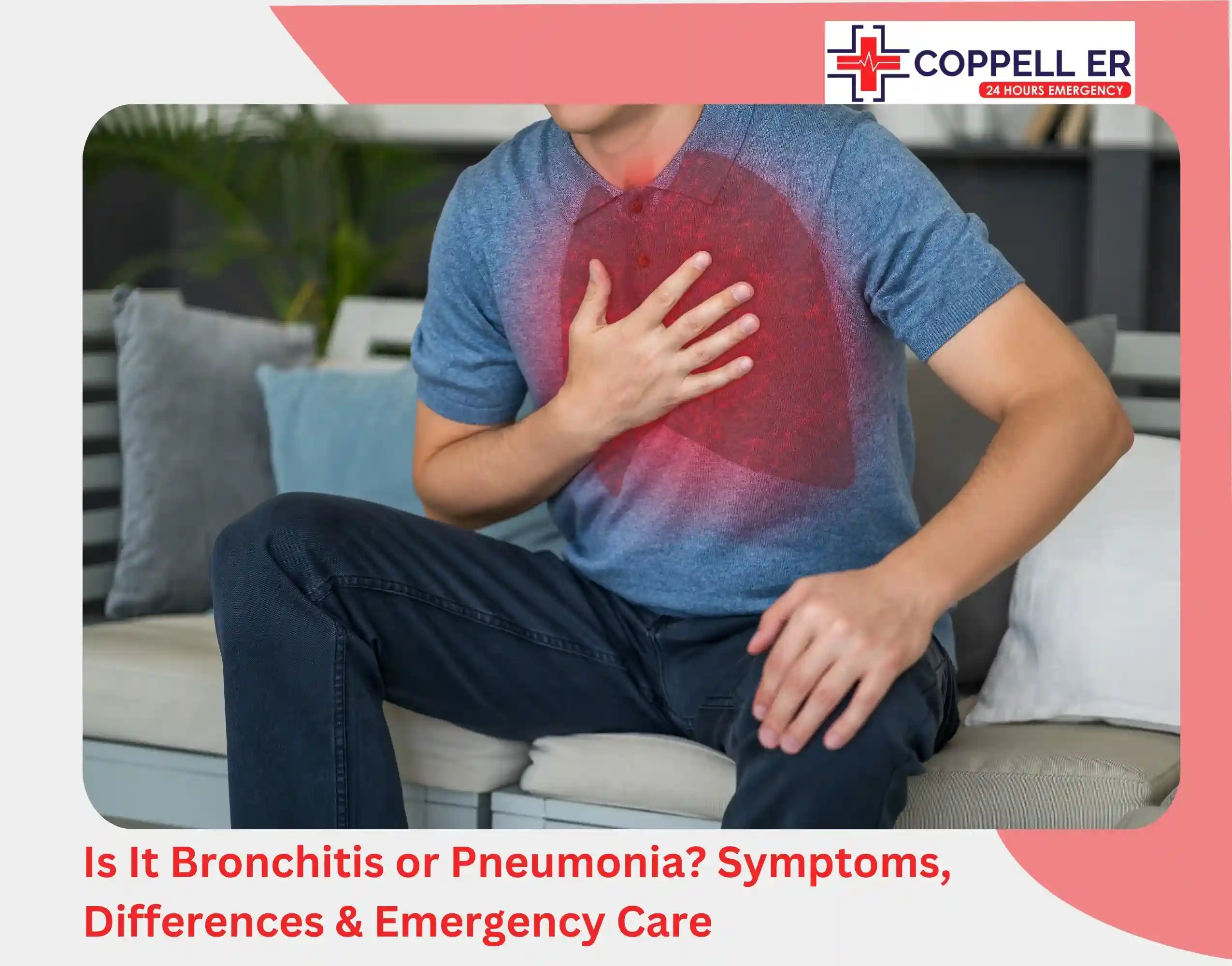
Abdominal pain is common in children and can have many different causes. Usually, abdominal pain goes away without treatment, but sometimes it is due to an underlying issue that needs specialized care.
Children can feel abdominal pain anywhere between the chest and the groin. This pain might be in one specific spot, spread out over a larger area, or feel like cramps. It’s prevalent in babies, infants, and those under 12.
Abdominal pain can stem from overeating, needing to use the restroom, or feeling anxious about an upcoming event. However, if your child often complains of abdominal pain, it’s difficult to know how to best help and when to seek medical advice.
This guide explores the causes of abdominal pain in children, including common triggers such as gastrointestinal issues, infections, and stress. It also discusses effective treatments for abdominal pain in children, emphasizing the importance of medical evaluation for accurate diagnosis and tailored care.
Guide to Abdominal Pain & Care
Causes of Abdominal Pain in Children
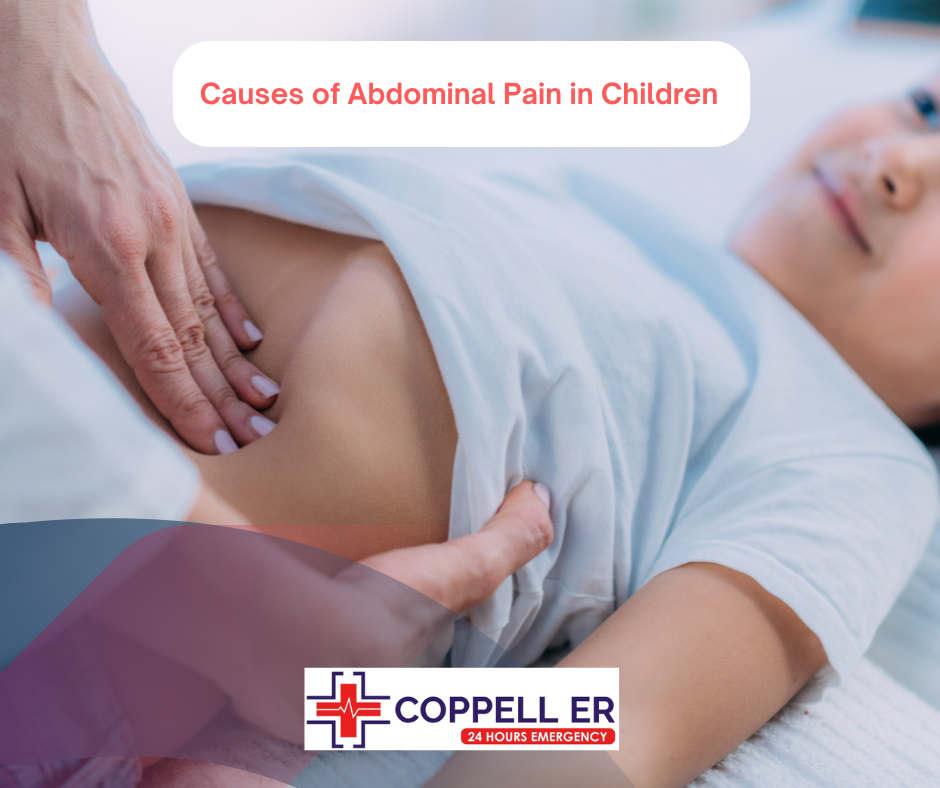
Abdominal pain in children can result from numerous causes. Recognizing these causes can assist in determining the right treatment and care. Here are some common reasons:
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Constipation: A frequent cause of abdominal discomfort and stomach pain in children.
- Gastroenteritis: Inflammation of the stomach and intestines, often due to infection.
- Food Intolerance or Allergies: Reactions to certain foods, like lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity, can cause chronic abdominal pain in children.
Infections
- Viral Infections: Such as colds or flu, which can lead to stomach aches.
- Bacterial Infections: Including conditions like strep throat, which may present with abdominal pain.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections in the urinary tract can cause lower abdominal pain in children.
Stress and Anxiety
- Emotional Distress: Anxiety about school, family issues, or social situations can manifest as functional abdominal pain in children.
- Upcoming Events: Nervousness about tests, performances, or new experiences can result in stomach aches.
Dietary Factors
- Overeating: Consuming large amounts of food can lead to abdominal discomfort.
- Junk Food: High-fat, sugary, or spicy foods can irritate the digestive system.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluids can cause stomach pain in children.
Medical Conditions
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic condition affecting the large intestine, causing cramping and functional abdominal pain in children.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Other Causes
- Menstrual Cramps: In adolescent girls, menstrual cycles can cause abdominal pain.
- Injuries: Trauma to the abdomen from accidents or sports injuries
Understanding these causes helps in providing appropriate care and knowing when to seek medical attention. If your child often complains of abdominal pain, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation, including the diagnosis of abdominal pain in children, and to receive the right treatment..
Symptoms to Look For in Pediatric Abdominal Pain
Understanding the symptoms and their characteristics can be essential in identifying potential issues and seeking appropriate medical care for pediatric abdominal pain. The cause can often be determined by observing these symptoms. Here are some key signs to watch for:
Location and Nature of Pain
- Widespread Pain: Could indicate stomach flu or constipation
- Lower Right Abdominal Pain: May suggest appendicitis
- Upper Abdominal Pain: Might be due to acid reflux or gastritis
Associated Symptoms
- Fever: Usually indicates an infection
- Vomiting and Diarrhea: Common with stomach flu
- Constipation: Hard, painful stools
- Rash: Could signal vascular inflammation
- Painful Urination: May indicate a urinary tract infection
Behavioral Changes
- Refusal to Eat
- Unusual moodiness or tiredness
- Changes in Sleep Patterns
Diagnosis of Abdominal Pain in Children

Diagnosing abdominal pain in children involves a comprehensive approach to uncovering its underlying cause. Here’s how healthcare providers typically proceed:
Medical History and Physical Examination
- History: Detailed questioning about when the pain started, its duration, location, and characteristics. They inquire about accompanying symptoms like fever, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and changes in urination.
- Physical Examination: Palpation of the abdomen to check for tenderness, swelling, or masses. They also assess vital signs and signs of dehydration.
Diagnostic Tests
Accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment of abdominal pain in children are essential for relieving symptoms and addressing any underlying medical conditions effectively. Some diagnostic approaches include:
- Blood Tests: Checking for signs of infection, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
- Urine or Stool Samples: Analyzing for infection or other issues.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound: Used to visualize organs such as the liver, kidneys, and appendix. It aids in diagnosing conditions like appendicitis or gallstones.
- X-ray: Typically used to identify issues such as bowel obstruction or foreign objects.
- CT Scan or MRI: Provides detailed images of the abdomen for complex cases requiring more information than ultrasound or X-ray can provide.
Specialized Procedures
- Endoscopy or Colonoscopy: Invasive procedures to directly view the digestive tract for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive surgery for direct examination and treatment of abdominal conditions.
Considering Differential Diagnosis
- Assessing various potential causes based on symptoms, medical history, and test results. This includes gastrointestinal issues (e.g., gastroenteritis, appendicitis) and non-gastrointestinal causes (e.g., urinary tract infections, gynecological conditions in adolescents).
Timely and accurate diagnosis, combined with appropriate treatment, is vital for managing abdominal pain in children. Using a comprehensive approach that includes medical history, physical examination, diagnostic tests, and specialized procedures, healthcare providers effectively identify the causes of abdominal pain in children and implement suitable treatments. This ensures the child’s well-being and quick recovery, alleviating discomfort and addressing any underlying health concerns.
Treatment for Abdominal Pain in Children
Managing pediatric abdominal pain involves identifying the cause and relieving symptoms. Common treatments include:
Medical Care
- Medications: Doctors prescribe antibiotics for infections, antacids for acid reflux, and anti-inflammatory drugs for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease.
- Hydration: Ensuring the child stays well-hydrated, especially if there is vomiting or diarrhea.
- Diet Adjustments: Modifying the child’s diet to avoid foods that could worsen the condition, such as dairy for lactose intolerance or fatty foods for gallbladder issues.
Home Remedies
- Encouraging rest to help alleviate stomach pain in children
- Applying a warm compress to ease abdominal discomfort
- Promoting mild activities, like walking, to help with constipation
In certain situations, surgical procedures may be recommended by doctors. Treating chronic abdominal pain in children, including cases of functional abdominal pain, demands a personalized approach that effectively relieves symptoms and targets the root causes.
If your child is experiencing abdominal discomfort, get expert pediatric care at ER of Coppell. We specialize in diagnosing and treating abdominal pain in children, including emergencies like appendicitis and gastroenteritis. We prioritize your child’s well-being with prompt evaluation and personalized treatment options tailored to their needs.
FAQs
When to worry about abdominal pain in children?
If your child has stomach pain that lasts more than a week, comes and goes, intensifies with nausea or vomiting, or shows no improvement within 24 hours, contact the ER promptly.
Which medicine is good for child stomach pain?
Gently massaging your child’s belly or engaging them with a book helps ease discomfort. Consider giving paracetamol or ibuprofen for pain relief, ensuring ibuprofen is taken with food or milk if it upsets the stomach.
What are the red flags for abdominal pain in children?
Red flags for abdominal pain in children include severe pain, accompanied by fever or vomiting, and noticeable changes in behavior, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.